what's the most common injury in youth soccer
 Common kids soccer
Common kids soccerinjury: the scraped knee.
The most common injury in youth soccer is caused by overuse. The list of injuries involving kids playing soccer includes tendonitis, shin splints, and stress fractures that will simply heal with the proper amount of rest. Of course recently, the most talked about safety issue lately mentioned in the news is head injury from concussion.
With soccer injuries, the most common body parts injured with children is wrist/finger/hand at 20.3%, ankles at 18.2%, and knee with 11.4%. The most common diagnoses for soccer-related injuries for kids were sprain/strain at 35.9%, bruises/abrasion at 24.1%, and fractures at 23.2% of all diagnoses.
This data comes from a study of 1.6 million pediatric soccer injuries reported on pubmed.gov. A statistical breakdown of soccer injuries in kids ages 2-18 was done. **Note that these medically diagnosed injuries don't include all the knee scrapes and brush burns that likely go unreported by soccer moms and dads everywhere.
most common injuries in youth soccer by body part
Kids can get injured from running, kicking, contact with another player, or even just simply slipping. That's one of the reasons it's a good idea to have well fitting soccer cleats.
Here are the 4 categories of soccer injuries that can occur from playing soccer.
1. injuries to fingers, wrists, and hands
 Arm Injury
Arm InjuryInjuries to young hands, wrists, and finger from soccer are likely the least reported and are likely the most common body part that is injured in youth soccer. Injury to these areas can easily occur from a fast moving soccer ball as well as from falling down and bracing your fall to the ground.
Although any injury can happen in a serious way, hand area injuries most likely to heal completely with no long term effects at all. The most common fracture in the wrist area is the buckle fracture that usually accompanies a fall.
2. ankle injuries
 Ankle support wrap
Ankle support wrapMost injuries in soccer occur with some aspect of the legs, whether it's up high with quadriceps, in the middle with the knee or calves, or down low, with the shins, ankles, or feet.
Ankle sprains happen with a large variety in how bad the injury is. Sprains can result in significant pain and swelling around the ankle and spread well into the foot as well. Most of the swell in usually occurs on the outside of the ankle rather than on the inside.
Young soccer players can also suffer from ankle fractures. The ankles of 10-15 year olds are most vulnerable to fractures because of the closing growth plates in the ankles. Many of these ankle fractures can be treated without needing an operation. Often a cast or a restrictive boot can work to heal the injury if no displacement has occurred.
Of course, bruises, scrapes and bumps of the ankle area are also common due to miss-kicks and ball misses.
3. knee injuries
 Kid's Knee Brace
Kid's Knee BraceSoccer involves a large amount of running, changing directions, pivoting, twisting, and sudden stopping. That makes it a great workout for kids, but it comes along with a high demand on the lower legs. The knees and the calves are at risk, for injury from both extreme stress as well as collisions.
ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) tears are the most feared in athletes, both young and old, because of the challenges that come along with repair and rehabilitation. The risk of ACL tears is between 4 and 8 times greater is female soccer players than males. These tears typically don't heal without surgery to stabilize the knee at return to basic functionality.
More common are the sprains and strains of both muscles and ligaments in these areas. many variables figure in to the risk of youth soccer injuries, including the weather, the specific conditions of the soccer field, as well as the equipment like protective gear, the goals and the pressure of the ball.
4. soccer head injuries
Even though it's gotten the most publicity, head injury from actually heading the soccer ball is much less likely the cause of head injuries from soccer. Injury is actually more frequently caused when 2 soccer players collide in some manner.
Despite the recent debates on whether the heading of the soccer ball should be banned in the younger age groups, most soccer-related head injuries do not result in a concussion.
Interestingly, male soccer players were more than twice as likely to sustain a head injury playing soccer as female soccer players.
Statistics on soccer head injuries from the British Journal of Sports Medicine on soccer injuries involving the head:
YOUTH SOCCER HEAD INJURIES
| PERCENTAGE | TYPE OF INJURY | |
| 24.7% | Open Wounds to the head. | |
| 18.7% | Categorized as superficial. | |
| 16.2% | Minor closed head injury | |
| 15.3% | Ocular injuries | |
| 14.0% | Concussion Injuries |
most common soccer injuries for preschool soccer
 Preschool Soccer
Preschool SoccerThe youngest soccer players rarely get seriously injured, but it can happen. In 12 years of running a soccer program for kids ages 2-6, with hundreds of kids enrolled every Fall, Winter, Springs, and Summer season, fortunately, I never had any reported serious injuries.
According to the PubMed study, In the group of children 2 to 4 years old playing youth soccer the kids sustained a higher proportion (41%) of face and head/neck injuries than the older kids did (15.5%; relative risk).
Why? It's likely that the young players have not yet developed the same level of balance and body control. Additionally, that automatic reaction to soften their fall and protect their heads/necks/faces by using their hands and arms is not developed as much as older soccer players. On a personal level I've notice this to be accurate in my 14 month old grandson.
youth soccer injuries vs. other sports
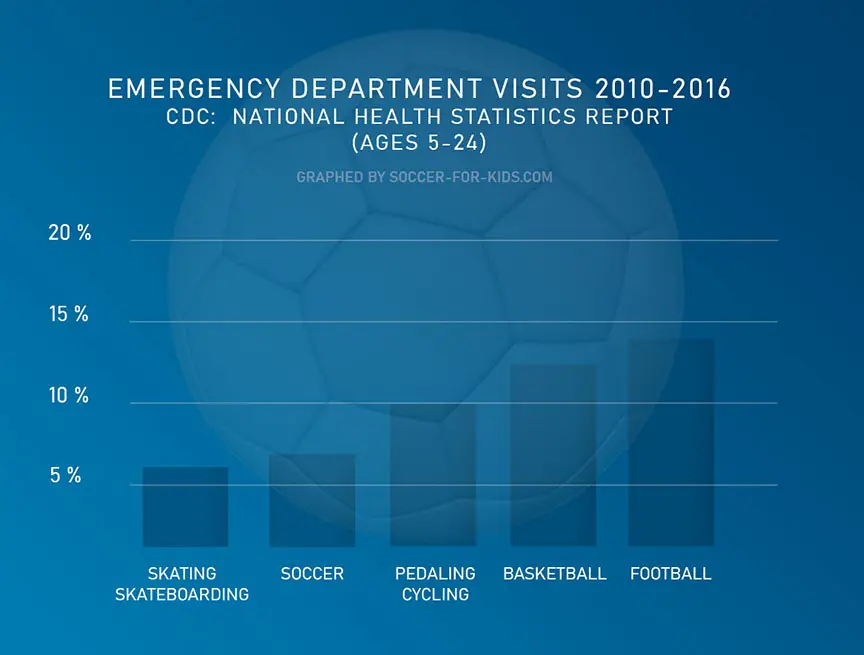
Although kids can get hurt playing soccer, it's not the most dangerous sport by any means. Statistical research by the CDC (Center for Disease Control) shows soccer came in 4th place for visits to emergency departments in the USA over a 7 year time span.
It's also interesting to note that in the 5 year old to 9 year old age group segment soccer did not even make the top 5 list for serious injuries. Despite the huge participation levels of kids playing soccer, only 3.1% of the visits to emergency departments were due to youth soccer, compared with 7.1% in the entire 5-24 age group, as shown in the bar graph above.
That means soccer risks are quite a bit less at the youngest of ages.
UnderHydration Injury

Although it's not technically an injury, this article on injuries would be incomplete without a few words about kids and hydration. The importance of proper hydration can't be overemphasized.
Hundreds of studies have shown the many health benefits of drinking water. A lack of fluids can lead to cramps and possible injuries. Dozens of studies have been done on the existing lack of hydration in soccer and other sports.
One way to combat this is to inspire our kids to develop lifelong good hydration habits on and off the soccer field. One great but simple step in this direction is to have a good water bottle available at all times. Here' my post on the best water bottle for kids.
final comments on youth soccer injuries
Kids can get injured in soccer, no doubt. There are always risks with any physical activity. That includes the school playground, your own backyard, and any other sport that involves movement. Sadly, children are at a much higher risk to die from a car crash, gun shot, cancer, suffocation, or drowning than from a sports injury.
Although probably not typical, my 3 kids played soccer from the time they were 5 years old through 18 years old and none of them ever had any injuries, only small doses of a little muscle soreness from hard training. I, on the other hand, had sprained ankles, sprained wrists, Lisfranc's joint inflammation, and pulled quadriceps muscles. All of these soccer injuries were during the 4 years I played high school soccer.
Keep soccer fun. Inspire safe soccer!


Soccer coach Bruce Lovelace started playing soccer in 1974 when, as a young boy, he constructed his own makeshift soccer goal. He played in high school, then in college and beyond. He started to coach his own children in the 1990s and then ran a Soccer Shots franchise for 12 years. Now, Coach Bruce publishes the soccer-for-kids.com website. Find out more about youth soccer coach Bruce Lovelace and what inspires this website.
Search for other youth soccer posts on this website:
Soccer-for-kids.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com